Manufacturing
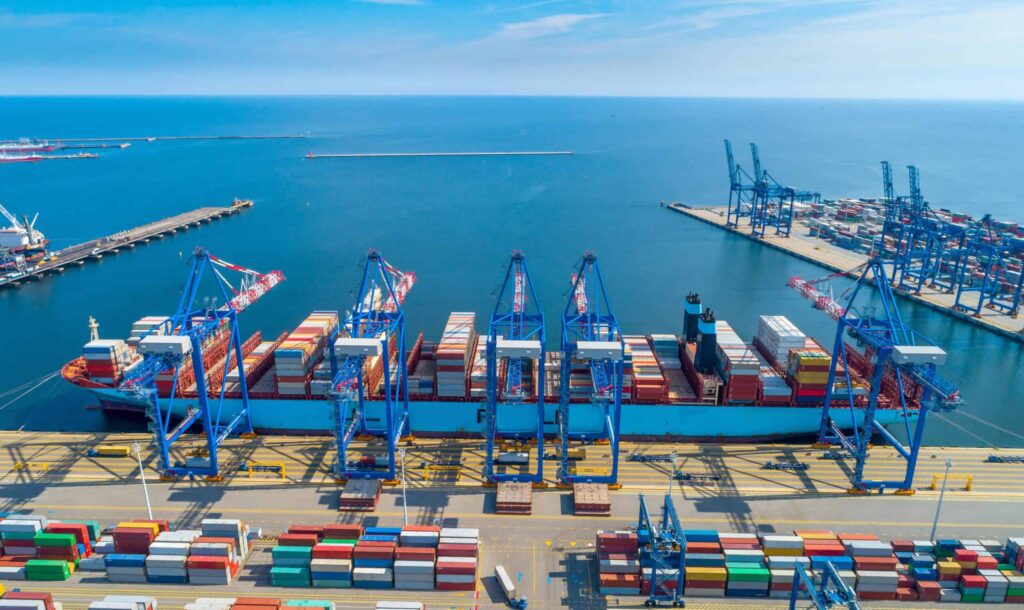
Baltic ports are undergoing significant transformations in 2025, positioning themselves as pivotal hubs in global trade and maritime innovation. Here’s an overview of the latest developments.
Strategic Investments and Modernization Efforts
• Latvia’s Port Development Roadmap: The Latvian government has introduced a comprehensive plan for 2025–2027 to enhance the competitiveness of its major ports—Riga, Ventspils, and Liepaja. This initiative aims to strengthen their roles in the national economy, transit, and logistics sectors.
• Klaipėda Port’s Infrastructure Upgrade: Lithuania’s Klaipėda Port is set to invest over €300 million in modern infrastructure, focusing on maritime business value creation and sustainability solutions. This investment underscores the port’s commitment to becoming an innovative hub for port services and green energy.
• Port of Gdańsk’s Expansion: Poland’s Port of Gdańsk is undertaking significant infrastructure projects, including the extension of rail and road connections to its handling terminals. These developments aim to accommodate the growing volumes of goods and adapt to dynamic changes in global supply chains.
Technological Advancements
• Freeport of Riga’s 5G Implementation: The Freeport of Riga has enhanced its maritime operations by deploying a 5G network, developed in partnership with telecom company LMT. This advancement facilitates real-time communication between the port, cargo ships, and autonomous sea drones, extending connectivity over 100 miles offshore.
Adaptation to Global Trade Dynamics
• Russia’s Baltic Port Expansion: In response to geopolitical challenges in the Black Sea, Russia is expanding its Baltic Sea ports, such as Vysotsky and Lugaport, to boost agricultural exports by 50% by 2030. These ports aim to handle up to 15 million tons annually, targeting new markets in Latin America and Africa.
Implications for Nordic Exporters
The modernization and strategic positioning of Baltic ports present new opportunities for Nordic manufacturers and exporters. Enhanced infrastructure and technological advancements facilitate more efficient trade routes, while the adaptation to global trade dynamics ensures resilience in the face of geopolitical shifts.